Maximizing Your PPC Campaigns: A Deep Dive into Key
Metrics
In the ever-evolving landscape of digital advertising,
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) campaigns stand as a powerful tool for businesses to
enhance their online visibility and drive conversions. However, success in PPC
advertising isn’t just about launching campaigns; it’s about understanding and
optimizing the metrics that drive performance. In this comprehensive guide,
we’ll explore essential PPC metrics and formulas that are crucial for achieving
campaign success.
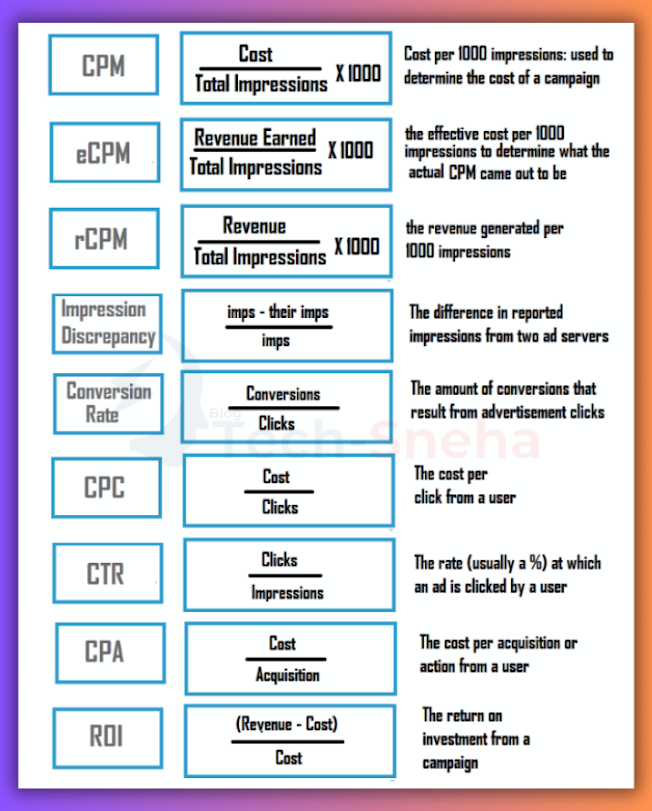
1. Cost per Click (CPC):
At the heart of PPC advertising lies the Cost per Click
(CPC) metric. CPC represents the average cost incurred for each click on an ad.
By dividing the total cost by the number of clicks, advertisers can gain
valuable insights into the efficiency of their ad spend. This metric is
essential for evaluating the effectiveness of ad campaigns and optimizing
budget allocation.
Formula: Cost / Clicks = CPC
2. Clickthrough Rate (CTR):
Clickthrough Rate (CTR) is a fundamental metric that
measures the percentage of users who clicked on an ad compared to the total
number of impressions. CTR serves as an indicator of ad performance and helps
advertisers gauge the relevance and effectiveness of their ad copy. A high CTR
suggests that the ad resonates with the audience, while a low CTR may indicate
the need for optimization.
Formula: Clicks / Impressions = CTR
3. Conversion Rate (CVR):
Conversion Rate (CVR) measures the percentage of ad clicks
that result in a desired conversion action, such as a purchase or sign-up. By
dividing the number of conversions by the total number of clicks, advertisers
can assess the effectiveness of their campaigns in driving desired outcomes.
CVR is a critical metric for evaluating campaign performance and optimizing
targeting strategies.
Formula: Conversions / Clicks = CVR
4. Cost Per Conversion (CPA):
Cost Per Conversion (CPA) quantifies the average amount of
money spent to acquire a single conversion. Whether it’s a lead, an inquiry, or
a purchase, CPA provides insights into the cost-effectiveness of advertising
campaigns. By dividing the total cost by the number of conversions, advertisers
can assess the efficiency of their marketing efforts and optimize budget
allocation accordingly.
Formula: Cost / Conversions = CPA
5. Cost Per Engagement (CPE):
Cost Per Engagement (CPE) measures the average cost incurred
for each engagement with an ad. This metric is particularly relevant for
platforms like Google Ads, where engagements include interactions such as
clicks on video ads or expansions of lightbox ads. By dividing the total cost
by the number of engagements, advertisers can evaluate the cost-effectiveness
of their ad campaigns and optimize targeting strategies.
Formula: Cost / Engagement = CPE
6. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS):
Return on Ad Spend (ROAS) is a key metric that evaluates the
effectiveness of advertising campaigns in generating revenue. ROAS measures the
ratio of revenue generated to the advertising spend incurred. A ROAS of 2, for
example, indicates that the revenue generated is twice the amount spent on
advertising. This metric helps advertisers assess the profitability of their
campaigns and make informed decisions about budget allocation.
Formula: Revenue / Cost = ROAS
7. Average Cost of Sale (ACOS):
Average Cost of Sale (ACOS) is a crucial metric for
businesses engaged in paid advertising on platforms like Amazon. ACOS represents
the percentage of revenue consumed by advertising spend. A high ACOS indicates
that a significant portion of revenue is being allocated to advertising costs,
potentially impacting profitability. By dividing the total advertising cost by
the revenue generated, advertisers can assess the efficiency of their
advertising campaigns and optimize budget allocation.
Formula: Cost / Revenue = ACOS
8. Impressions to Conversion Percentage:
Impressions to Conversion Percentage measures the percentage
of times a conversion action occurs compared to the number of times an ad is
shown. This metric provides insights into the relevance and effectiveness of ad
targeting. A low impression to conversions percentage may indicate poor keyword
relevancy or targeting strategies, necessitating optimization.
Formula: Conversions / Impressions = Impressions to
Conversions%
9. Revenue per Click:
Revenue per Click measures the average revenue generated per
click on an ad. This metric is invaluable for making informed bidding decisions
and optimizing ROI. By dividing the total revenue by the number of clicks,
advertisers can assess the profitability of their advertising campaigns and
adjust bidding strategies accordingly.
Formula: Revenue / Clicks = Revenue per Click
10. Revenue per Impression:
Revenue per Impression quantifies the average revenue
generated per ad impression. While not all impressions lead to conversions,
this metric provides insights into the value of each impression produced. By
dividing the total revenue by the number of impressions, advertisers can assess
the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns and optimize targeting
strategies.
Formula: Revenue / Impressions = Revenue per Impression
11. Average Order Value (AOV):
Average Order Value (AOV) measures the average amount spent
when a conversion occurs. This metric is essential for understanding customer
behavior and optimizing marketing strategies. By dividing the total revenue by
the number of conversions, advertisers can assess the average value of each
transaction and tailor their campaigns accordingly.
Formula: Revenue / Conversions = AOV
12. Cost per View (CPV):
Cost per View (CPV) is a metric commonly used to evaluate
the performance of video advertising campaigns. CPV measures the average cost
incurred for each video view. By dividing the total cost by the number of
views, advertisers can assess the cost-effectiveness of their video ad
campaigns and optimize budget allocation.
Formula: Cost / Views = CPV
13. Impression Share:
Impression Share measures the percentage of impressions
received compared to the total number of impressions available. This metric is
valuable for assessing the reach and visibility of ad campaigns. By dividing
the total impressions by the total available impressions, advertisers can gauge
their ad’s performance relative to the competition and identify opportunities
for increased exposure.
Formula: Impressions / Total Available Impressions =
Impression Share
14. Bid based on a CPA target:
Bid based on a CPA target enables advertisers to calculate
the maximum amount they can bid while adhering to a predefined CPA target. By
multiplying the Conversion Rate (CVR) by the CPA target, advertisers can
determine the maximum allowable bid to maintain profitability.
Formula: CVR * CPA Target = Maximum CPA Bid
15. Bid based on ROAS target:
Bid based on ROAS target allows advertisers to calculate the
maximum CPC with a ROAS model. By multiplying the Conversion Rate (CVR) by the
Average Order Value (AOV) and dividing by the ROAS target, advertisers can
determine the maximum allowable bid to achieve their desired ROAS.
Formula: (CVR * AOV) / ROAS Target = Maximum ROAS Bid
16. Bid based on ACOS target:
Bid based on ACOS target enables advertisers to calculate
the maximum allowable bid to maintain profitability while adhering to a
predefined ACOS target. By multiplying the Conversion Rate (CVR) by the Average
Order Value (AOV) and the ACOS target, advertisers can determine the maximum
allowable bid.
Formula: (CVR * AOV) * ACOS Target = Maximum ACOS Bid
17. Extra traffic from increasing budget to remove Lost IS
(Budget):
Extra traffic from increasing budget to remove Lost IS
(Budget) allows advertisers to
estimate the additional clicks and conversions they could receive by increasing
their budget to remove lost impression share due to budget constraints.
Formula: (Impressions Lost IS (Budget) * CTR) = Clicks
Lost
Clicks Lost * CPC = Money Not Spent
Clicks Lost * CVR = Conversions Lost
Conversions Lost * AOV = Revenue Lost
18. Performance if bids are increased to remove Lost IS (Rank):
Performance if bids are increased to remove Lost IS (Rank)
enables advertisers to estimate the potential performance improvements if bids
are increased to eliminate lost impression share due to rank.
Formula: (Impressions * (1 + Impression Share Lost IS
(Rank))) = Total Available Impressions
Old CPC * (1 + Impression Share Lost IS (Rank)) = New CPC
19. Project conversions, revenue, CPA, and ROAS from
clicks, CPC, CVR, and AOV:
Projecting conversions, revenue, CPA, and ROAS from clicks,
CPC, CVR, and AOV allows advertisers to forecast campaign performance based on
key metrics.
Formula: Clicks * CVR = Projected Conversions
Projected Conversions * CPC = Projected Cost
Projected Cost / Projected Conversions = Projected CPA
Projected Conversions * AOV = Projected Revenue
Projected Revenue / Projected Cost = Projected ROAS
20. Projections with an allocated budget:
Projections with an allocated budget enable advertisers to
forecast campaign performance within a specified budget.
Formula: Budget / CPC = Clicks
Clicks * CVR = Conversions
Conversions / Cost = CPA
Conversions * AOV = Revenue
21. Ad rank:
Ad rank is a metric used by search engines to determine the
position of ads in search results. It is calculated based on the Quality Score
and maximum bid of an ad.
Formula: Quality Score * Maximum Bid = Ad Rank
22. New CPC if Quality Score is improved:
New CPC if Quality Score is improved allows advertisers to
estimate the potential decrease in CPC if the Quality Score of an ad is
improved.
Formula: (Current Ad Rank / New Quality Score) = New CPC
23. Project month performance partway through the month:
Project month performance partway through the month enables
advertisers to forecast campaign performance based on average daily performance
from the previous seven days.
Formula: (Last 7 Days Cost / 7) = Last 7 Days Daily
Average Cost
Month So Far Cost + (Number of Days Remaining in Month *
Last Week Daily Average Cost) = Monthly Projected Cost
24. Monthly CVR change due to seasonality:
Monthly CVR change due to seasonality enables advertisers to
forecast changes in conversion rates based on historical data.
Formula: (Current Month CVR from Last Year / Last Month
CVR from Last Year) = Percentage Difference in CVR
Percentage Difference in CVR * Last Month CVR = This Month’s
Projected CVR
25. Bid modifier for device/location/audience/gender/age:
Bid modifier for device/location/audience/gender/age allows
advertisers to adjust bids based on performance metrics for specific segments.
Formula: (Specific Segment CVR / Total CVR) / Percentage
Bid Adjustment for Specific Segment
26. Convert CPM to price per impression:
Convert CPM to price per impression allows advertisers to
calculate the cost per impression for campaigns charged on a CPM basis.
Formula: CPM Cost / 1,000 = Cost per Impression
By understanding and effectively leveraging these key PPC
metrics and formulas, advertisers can optimize their campaigns for maximum
performance and ROI, ultimately driving business success in the competitive
digital landscape.